04. Implementing KD-Tree
Header Text
Implementing KD-Tree
ND312 C1 L3 A11 Implementing KD-Tree [LB]
Implementing KD Tree
A KD-Tree is a binary tree that splits points between alternating axes. By separating space by splitting regions, nearest neighbor search can be made much faster when using an algorithm like euclidean clustering. In this quiz you will be looking at a 2D example, so the the tree will be a 2D-Tree. In the first part of the quiz you will be working from
src/quiz/cluster/kdtree.h
and filling in the function
insert
which takes a 2D point represented by a vector containing two floats, and a point ID. The ID is a way to uniquely identify points and a way to tell which index the point is referenced from on the overall point cloud. To complete the
insert
function let's first talk about how a KD-Tree splits information.
Inserting Points into the Tree
Data
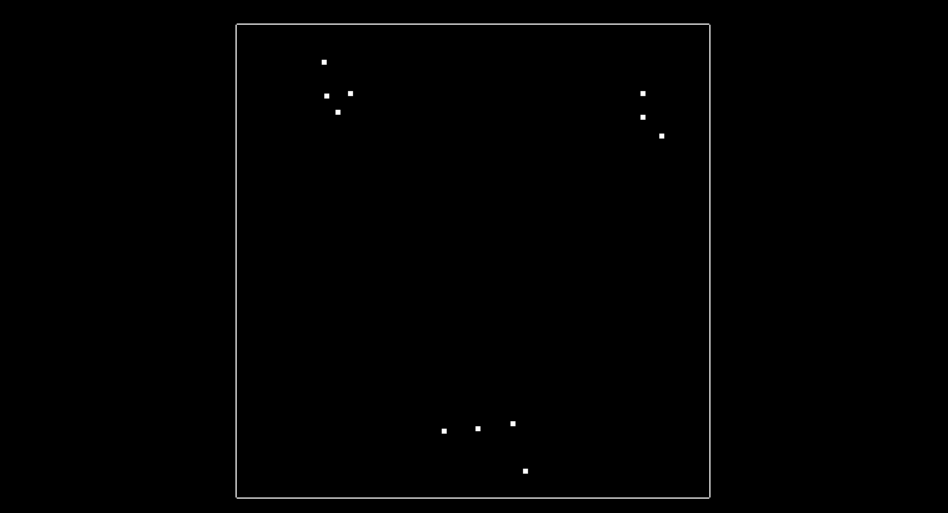
2D points to cluster
Building KD-Tree
The image above shows what the 2D points look like. In this simple example there are only 11 points, and there are three clusters where points are in close proximity to each other. You will be finding these clusters later.
In
src/quiz/cluster/cluster.cpp
there is a function for rendering the tree after points have been inserted into it. The image below shows line separations, with blue lines splitting x regions and red lines splitting y regions. The image shows what the tree looks like after all 11 points have been inserted, and you will be writing the code to do this over the next concepts.
Built KD-Tree
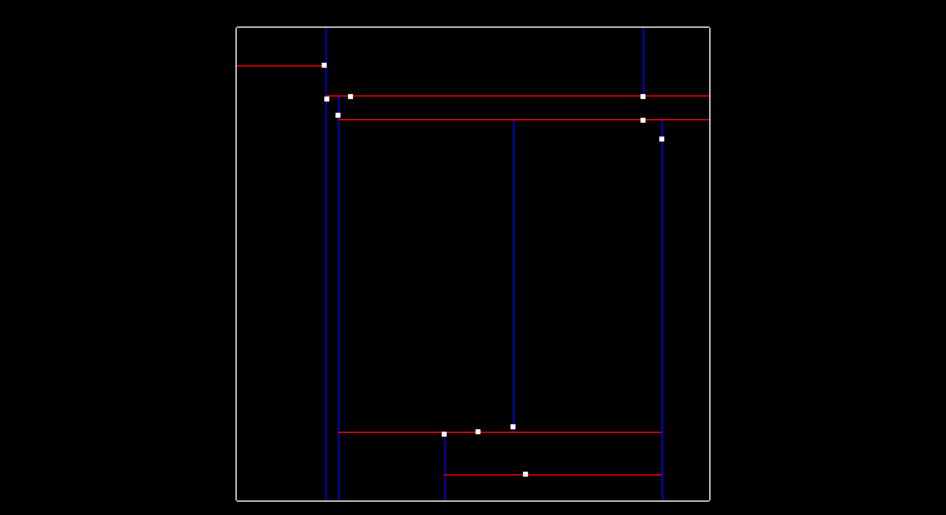
Tree separating x and y regions.